BMI Calculator
What is BMI and How is it Calculated?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple calculation used to determine whether an individual’s weight is appropriate for their height. It is commonly used as a screening tool to identify weight categories that may lead to health problems.
Formula:
BMI = Weight (kg) / [Height (m)]²
For example, if your weight is 70 kg and your height is 175 cm (1.75 m), your BMI will be calculated as follows:
BMI = 70 / (1.75 × 1.75) = 22.86
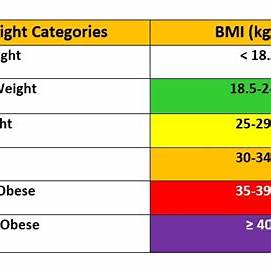
Based on the calculated BMI, here are the standard categories:
- Underweight: Less than 18.5
- Normal weight: Between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: Between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: 30 or more
Please note that BMI has some limitations. It does not differentiate between muscle and fat mass, and it may not be accurate for athletes, children, or older adults.

Body Mass Index: Everything You Need to Know
Body Mass Index (BMI) is one of the most commonly used health metrics to assess whether a person is underweight, of normal weight, overweight, or obese. It’s a simple calculation using height and weight, but it can provide important insights into potential health risks. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore what BMI is, how to calculate it, its health implications, and its limitations.
What is BMI?
The Definition of BMI
BMI, or Body Mass Index, is a numerical value derived from a person’s weight and height. It’s calculated using the formula:
BMI = Weight (kg) / [Height (m)]²
The Purpose of BMI
BMI serves as a screening tool to categorize individuals into weight groups such as underweight, normal weight, overweight, or obese. It’s widely used by healthcare providers to assess potential risks associated with weight-related conditions.
How to Calculate BMI
Manual Calculation
To calculate BMI manually, you need your weight in kilograms and your height in meters. Divide your weight by the square of your height.

Example Calculation
For example, if someone weighs 70 kg and is 1.75 meters tall, their BMI would be:
BMI = 70 / (1.75 × 1.75) = 22.86
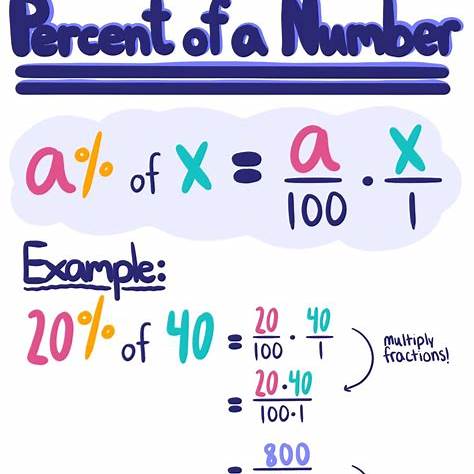
Using Online BMI Calculators
Many websites and apps provide free BMI calculators where you simply input your height and weight. These tools are quick, easy, and eliminate the need for manual calculations.
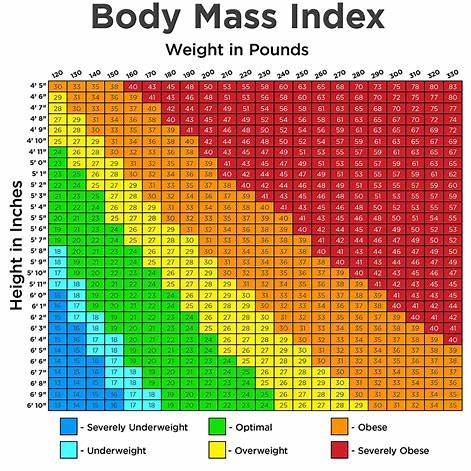
Interpreting BMI Results
BMI Categories
- Underweight: BMI less than 18.5
- Normal weight: BMI between 18.5 and 24.9
- Overweight: BMI between 25 and 29.9
- Obese: BMI 30 or greater
Health Implications of BMI
BMI can provide insights into health risks. For example:
Underweight: Increased risk of malnutrition and weakened immunity.
Overweight: Higher likelihood of cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
Obesity: Strong correlation with chronic illnesses such as hypertension, joint problems, and certain cancers.
Limitations of BMI
Does Not Account for Body Composition
BMI doesn’t distinguish between muscle mass and fat. For instance, athletes with high muscle mass may have a high BMI but low body fat.
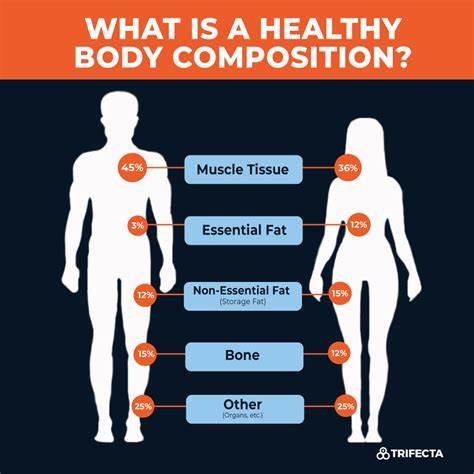
Ignores Fat Distribution
BMI cannot reveal where fat is distributed on the body. Central obesity, or fat around the abdomen, is a greater risk factor than fat distributed elsewhere.
Generalized for Age and Gender
BMI doesn’t consider differences in age, gender, or ethnicity. For example, older adults may have higher body fat percentages even with a normal BMI.
Using BMI Alongside Other Measurements
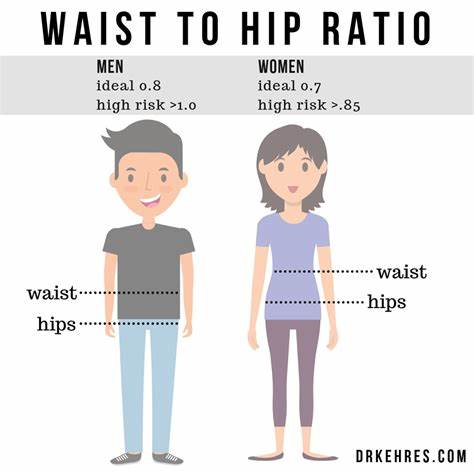
1. Waist-to-Hip Ratio
This ratio provides insights into fat distribution. A higher ratio suggests a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases.
2. Body Fat Percentage
Measuring body fat percentage can give a clearer picture of body composition compared to BMI alone.
3. Blood Pressure and Cholesterol
Combine BMI with these health metrics for a more comprehensive assessment of health risks.
Maintaining a Healthy BMI
1. Balanced Nutrition
Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Avoid excessive sugar and processed foods.
2. Regular Exercise
Engage in a combination of aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility workouts to maintain a healthy BMI.
3. Monitor Weight Regularly
Keep track of your weight and BMI periodically to identify any trends and take corrective action if necessary.

4. Manage Stress
High stress can lead to unhealthy eating habits and weight gain. Incorporate relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
Conclusion
While BMI is a valuable starting point for understanding weight-related health risks, it should not be used in isolation. Combining BMI with other metrics and consulting healthcare professionals can provide a clearer picture of overall health. By maintaining a healthy BMI through proper nutrition, regular exercise, and mindful living, you can improve your quality of life and reduce the risk of chronic illnesses.
Start tracking your BMI today to take charge of your health and wellness journey!